Training Pdf Files - Guide
Objective
The following is a guide on fine-tuning a model with pdf documents for text generation on Emissary, specifically focusing on Llama-3.2-3B-Completion and similar models that support text generation tasks.
Data Preparation: Converting PDFs to JSONL Format
Fine-tuning on PDFs requires first extracting text from the documents and then structuring the data in JSONL format.
Step 1: Extract Text from PDFs
Method 1: Using PyMuPDF (fitz)
import fitz # PyMuPDF
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
doc = fitz.open(pdf_path)
text = "\n".join([page.get_text("text") for page in doc])
return text
pdf_text = extract_text_from_pdf("document.pdf")
print(pdf_text[:1000]) # Print first 1000 characters
Method 2: Using PDFPlumber (for complex PDFs)
import pdfplumber
def extract_text_pdfplumber(pdf_path):
text = ""
with pdfplumber.open(pdf_path) as pdf:
for page in pdf.pages:
text += page.extract_text() + "\n"
return text
pdf_text = extract_text_pdfplumber("document.pdf")
Method 3: Using OCR for Scanned PDFs (Tesseract)
import pytesseract
from pdf2image import convert_from_path
def extract_text_from_image_pdf(pdf_path):
images = convert_from_path(pdf_path)
text = "\n".join([pytesseract.image_to_string(img) for img in images])
return text
pdf_text = extract_text_from_image_pdf("document.pdf")
Step 2: Clean and Preprocess Extracted Text
import re
def clean_text(text):
text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text) # Remove excessive spaces
text = re.sub(r'[^\x00-\x7F]+', ' ', text) # Remove non-ASCII chars
return text.strip()
cleaned_text = clean_text(pdf_text)
Step 3: Convert Extracted Text to JSONL Format
Sentence-Level Formatting
import json
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
nltk.download("punkt")
def split_into_prompt_completion(text):
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
json_data = []
for i in range(len(sentences) - 1):
json_data.append({"prompt": sentences[i], "completion": sentences[i + 1]})
return json_data
json_data = split_into_prompt_completion(cleaned_text)
with open("train.jsonl", "w") as f:
for entry in json_data:
f.write(json.dumps(entry) + "\n")
Paragraph-Level Formatting with Context-Length Splitting
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
import json
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import sent_tokenize
nltk.download("punkt")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B")
def split_text_into_chunks(text, max_length=2048):
tokens = tokenizer.encode(text)
chunks = []
for i in range(0, len(tokens), max_length):
chunk_tokens = tokens[i:i + max_length]
chunk_text = tokenizer.decode(chunk_tokens)
sentences = sent_tokenize(chunk_text)
if len(sentences) > 1:
chunks.append(sentences)
return chunks
def format_chunks_with_prompt_completion(text, max_length=2048):
chunks = split_text_into_chunks(text, max_length)
json_data = []
for sentences in chunks:
prompt = sentences[0]
completion = " ".join(sentences[1:])
json_data.append({"prompt": prompt, "completion": completion})
return json_data
json_data = format_chunks_with_prompt_completion(cleaned_text)
with open("train.jsonl", "w") as f:
for entry in json_data:
f.write(json.dumps(entry) + "\n")
Choosing the Right Splitting Method
| Splitting Type | Recommended Use Case |
|---|---|
| Sentence-Level Splitting | Best for short, independent text completions or tasks requiring precise language modeling. |
| Paragraph-Level Splitting | Suitable for maintaining contextual meaning, useful for paragraph-based text generation. |
| Full Document Splitting | Used when training on long-context models that require full document context preservation. |
Finetuning Preparation: Converting PDFs to JSONL Format
Please refer to the in-depth guide on Finetuning on Emissary here - Quickstart Guide.
Create Model Service
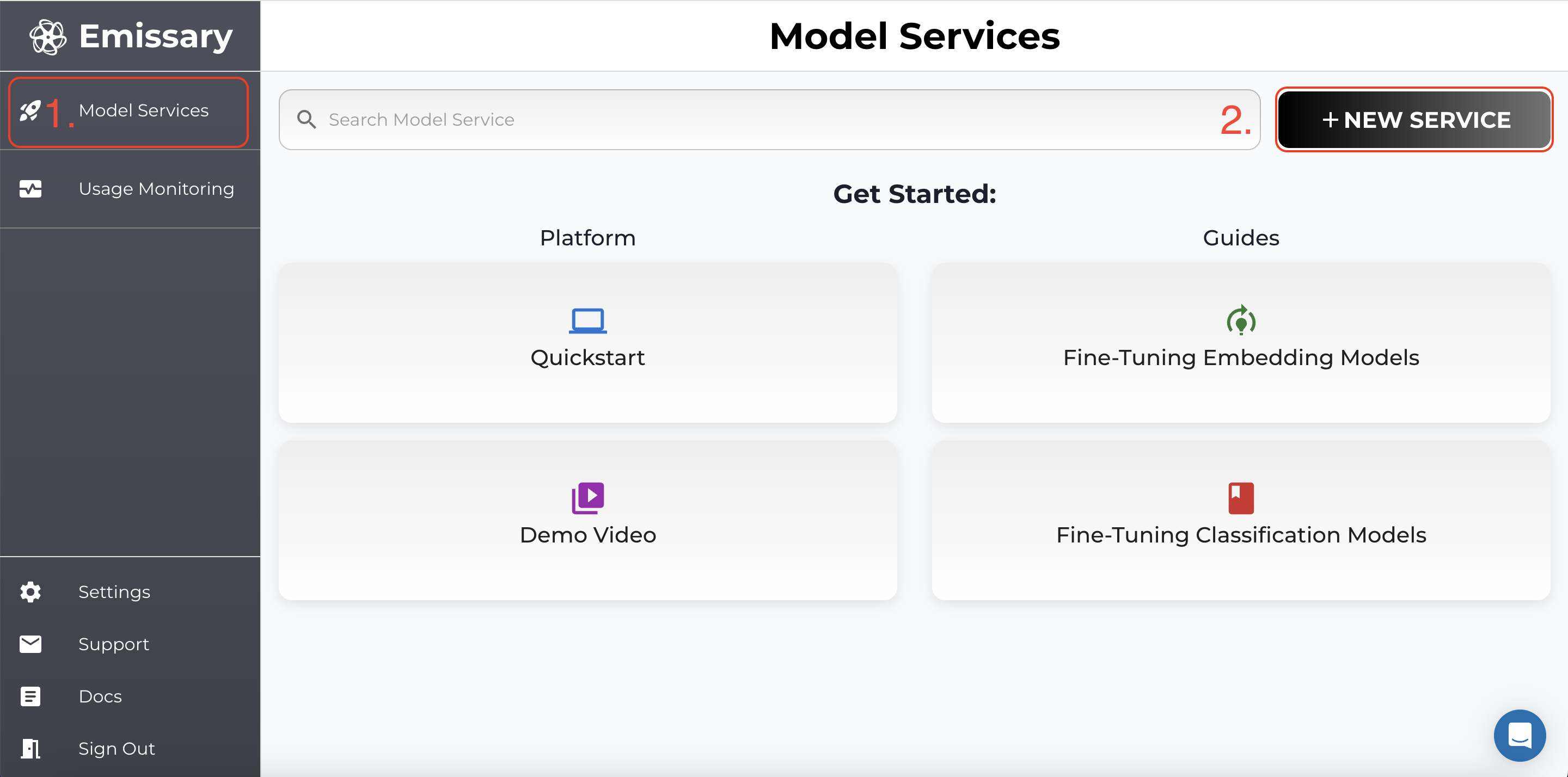
Navigate to Dashboard arriving at Model Services, the default page on the Emissary platform.
- Click + NEW SERVICE in the dashboard.
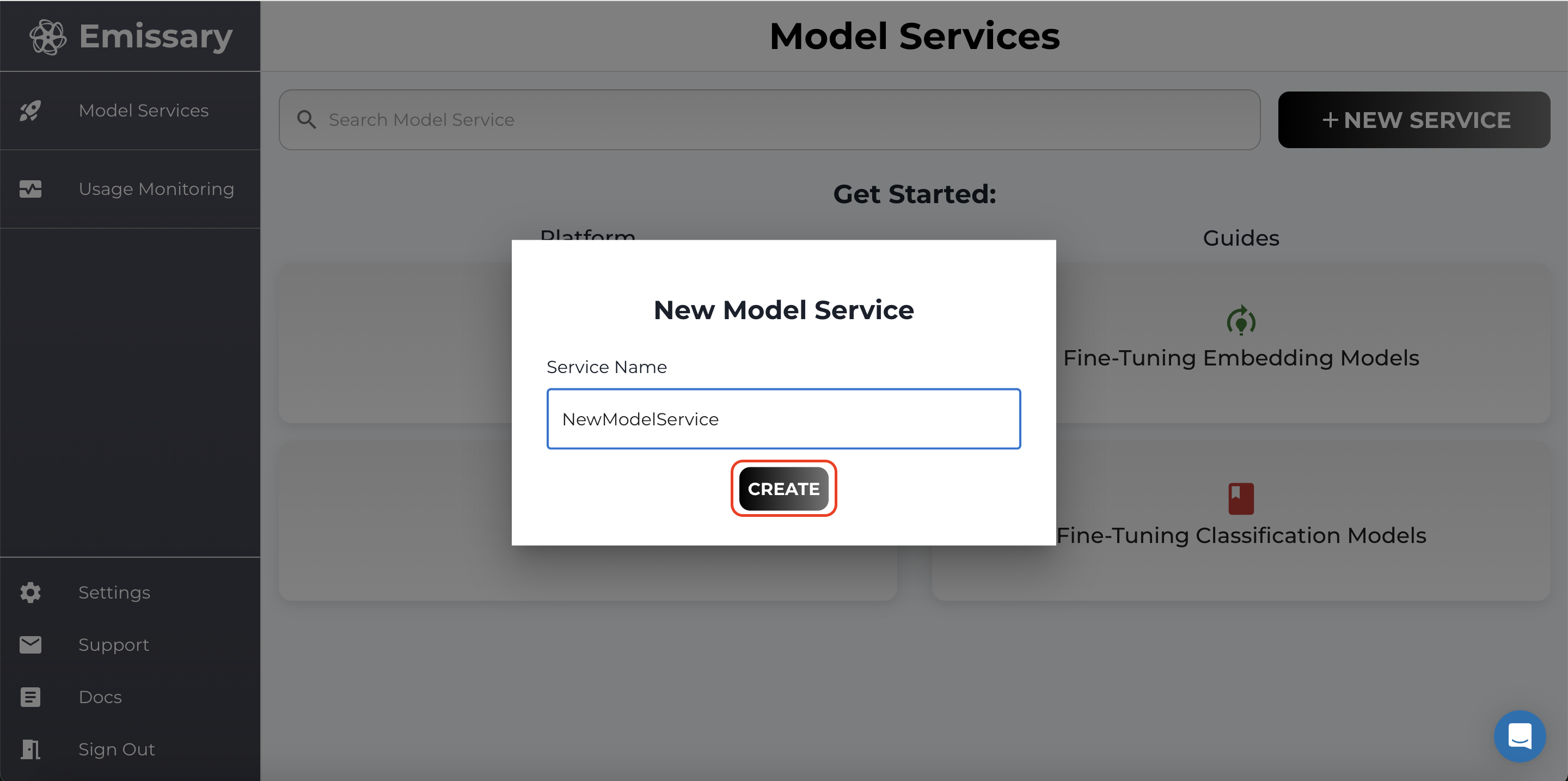
- In the pop-up, enter a new model service name, and click CREATE.
Uploading Datasets
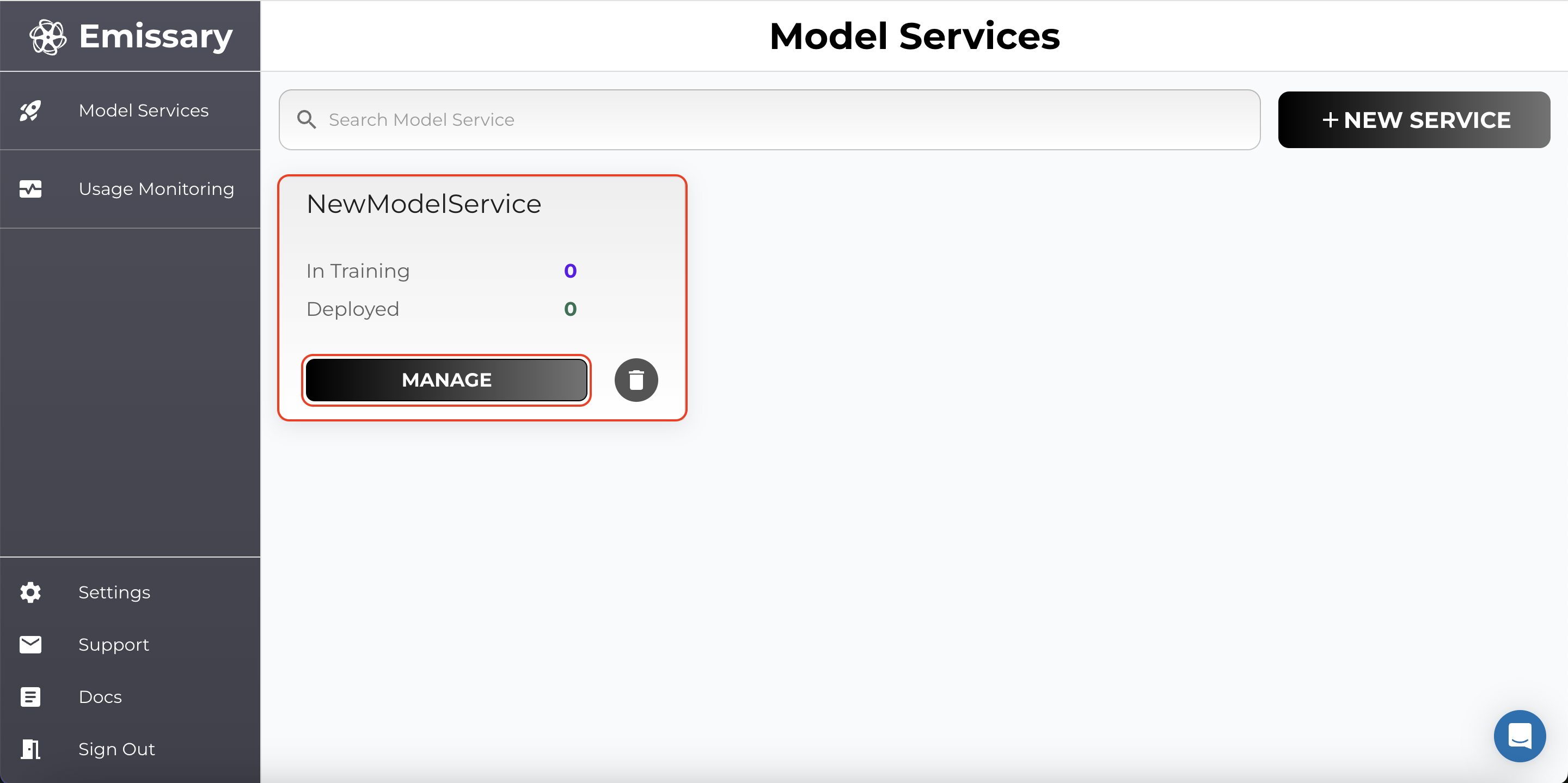
A tile is created for your task. Click Manage to enter the task workspace.
- Click MANAGE in the Datasets Available tile.
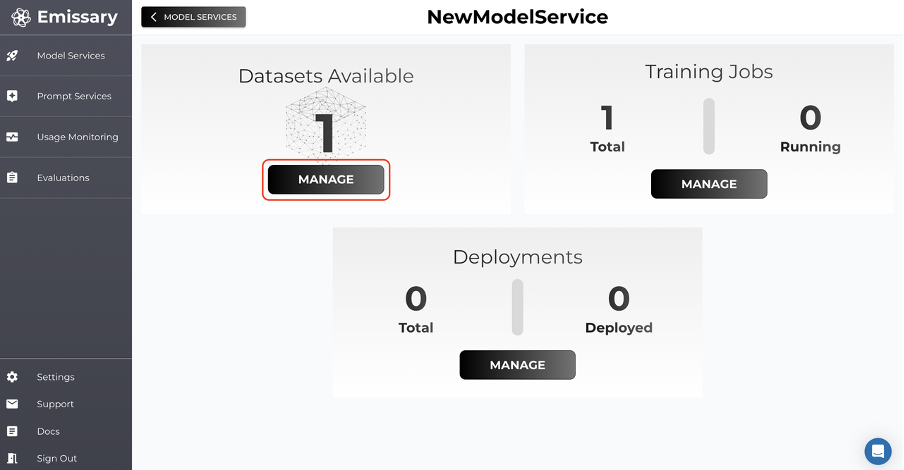
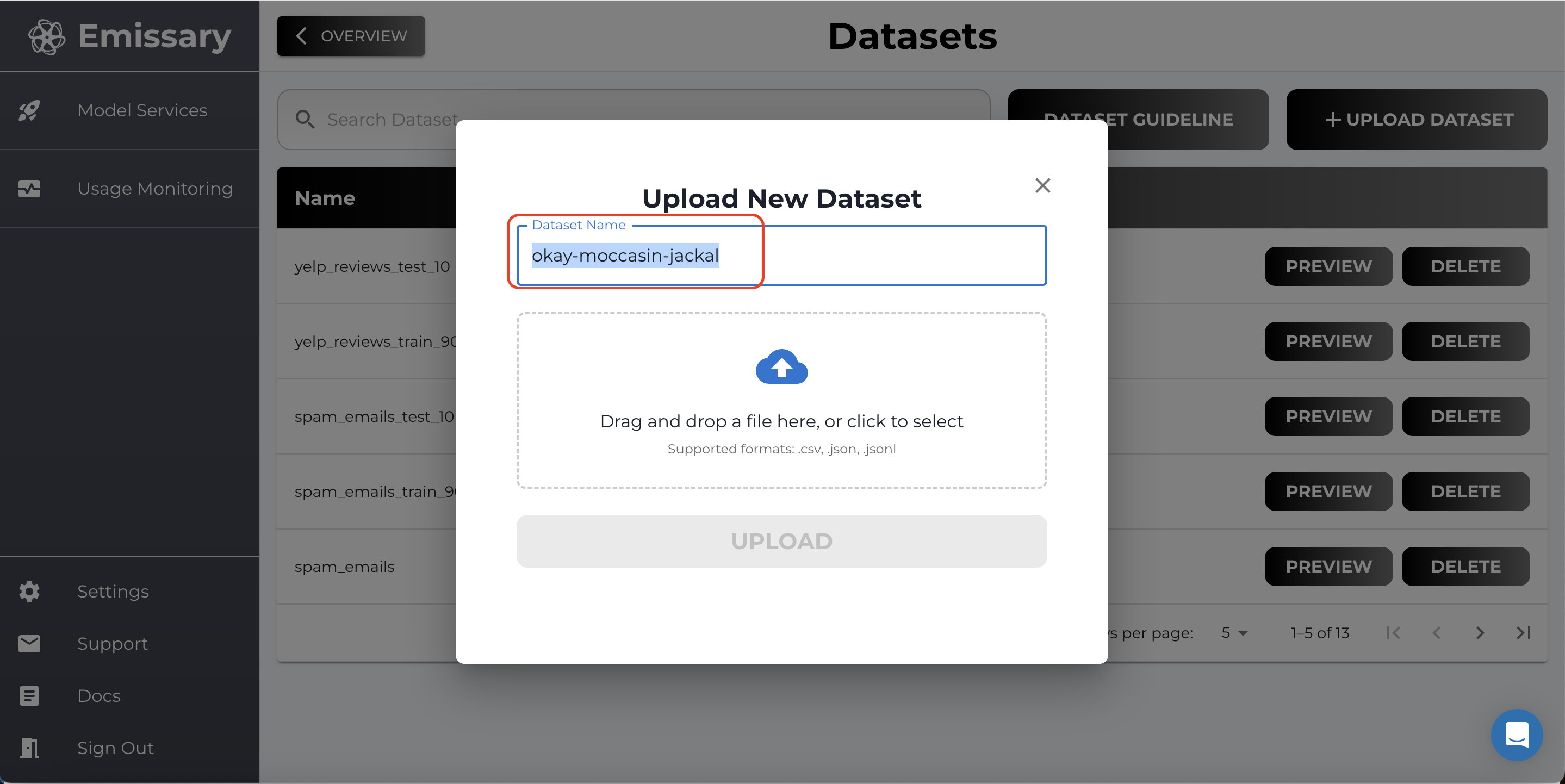
- Click on + UPLOAD DATASET and select training and test datasets.
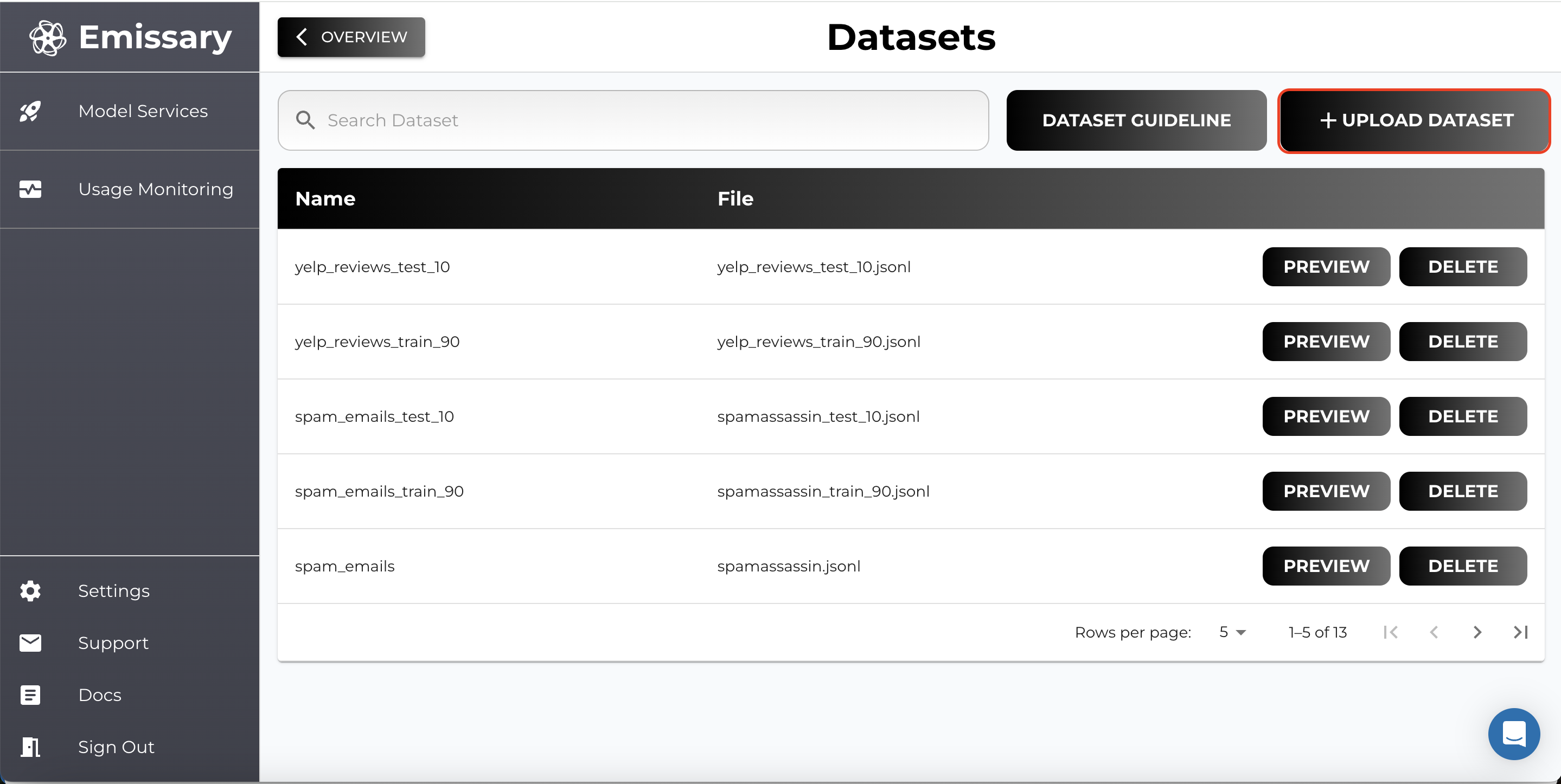
- Name datasets clearly to distinguish between training and test data (e.g., extraction_train_jsonl, extraction_test_jsonl).
Important Note: For LLM models, it is recommended to use JSON Lines (.jsonl) format.
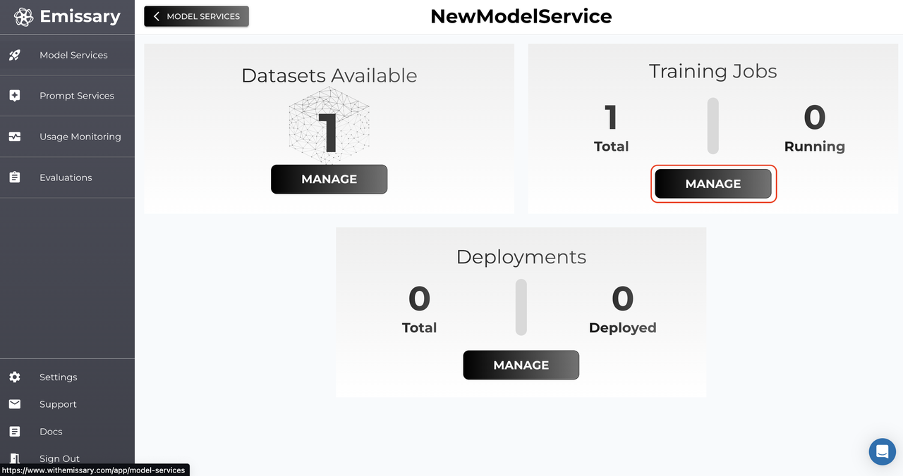
Model Finetuning
Now, go back one panel by clicking OVERVIEW and then click MANAGE in the Training Jobs tile.
Here, we’ll kick off finetuning. The shortest path to finetuning a model is by clicking +NEW TRAINING JOB, naming the output model, picking a backbone (base model), selecting the training dataset (you must have uploaded it in the step before), and finally hitting START NEW TRAINING JOB.
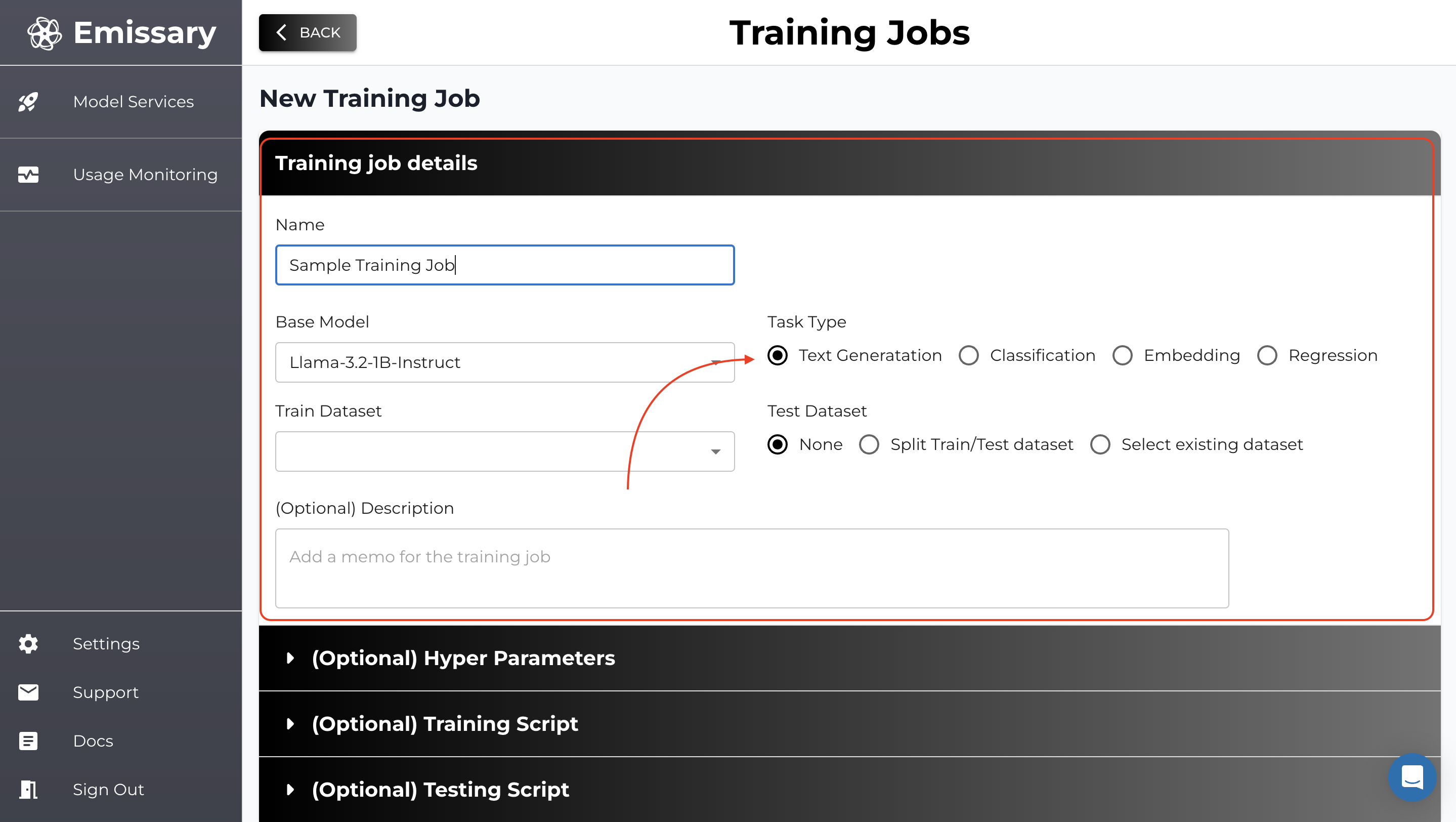
Selecting Base Model
-
You can select base model from the dropdown, the Llama 3.2-3B-Completion model is recommended for starting experiments.
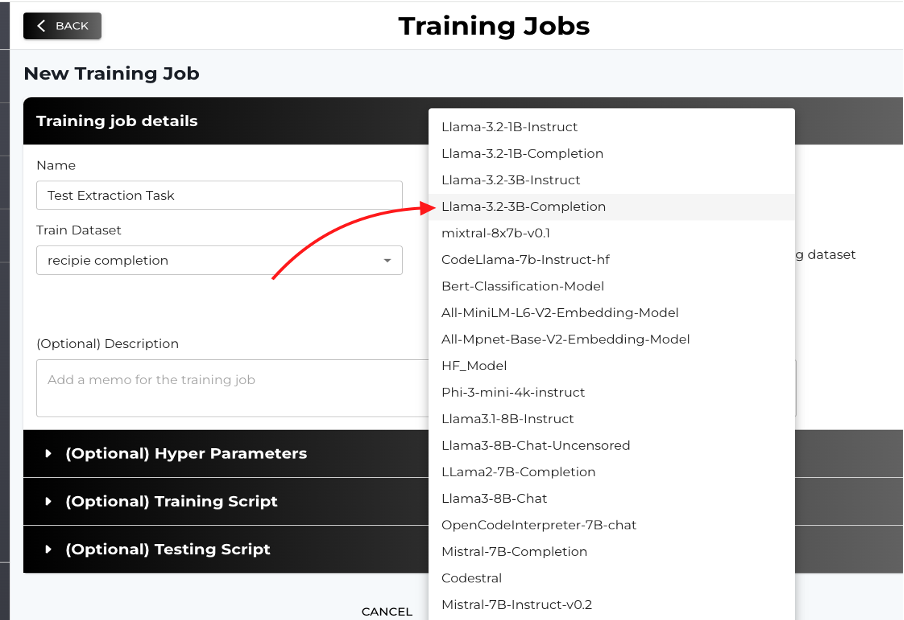
-
A custom function that compares two strings and gives a matching fuzzy score has been provided. Uncomment Fuzzy match to use.
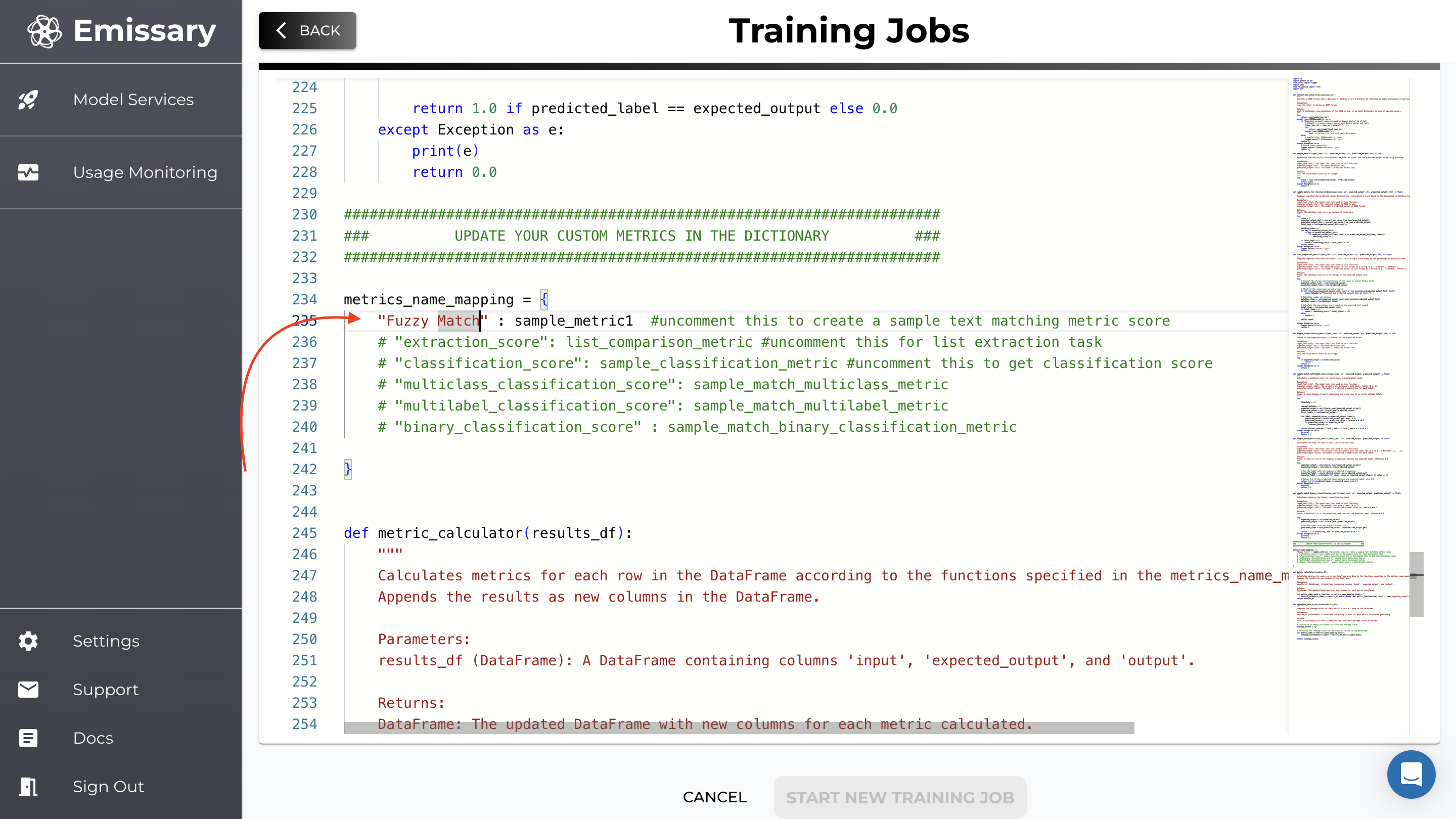
Training Parameter Configuration
Please refer to the in-depth guide on configuring training parameters here - Finetuning Parameter Guide.
Model Monitoring & Evaluation
Using Test Datasets
Including a test dataset allows you to evaluate the model's performance during training.
- Per Epoch Evaluation: The platform evaluates the model at each epoch using the test dataset.
- Metrics and Outputs: View evaluation metrics and generated outputs for test samples.
- Post completion of training, check results in Training Job --> Artifacts.
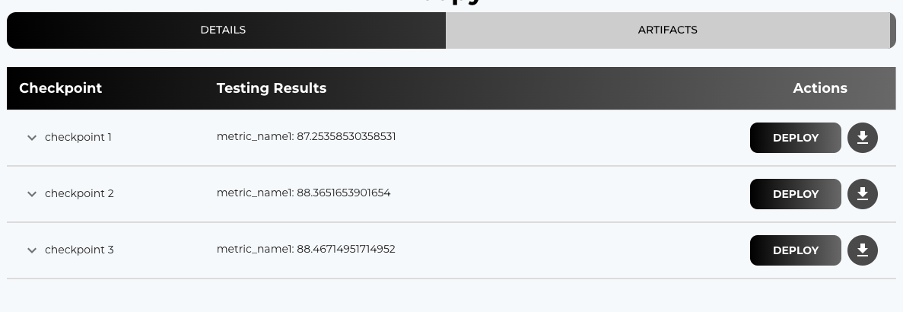
Evaluation Metric Interpretation
- Accuracy: Indicates the percentage of correct predictions.
- F1 Score: Balances precision and recall; useful for imbalanced datasets.
- Custom Metrics: Define custom metrics in the testing script to suit your evaluation needs.
Deployment
Refer to the in-depth walkthrough on deploying a model on Emissary here - Deployment Guide.
Deploying your models allows you to serve them and integrate them into your applications.
Finetuned Model Deployment
- Navigate to the Training Jobs Page. From the list of the finetuning jobs, select the one you want to deploy.
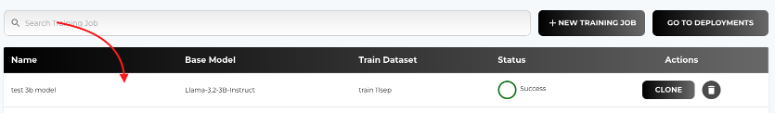
- Go to the ARTIFACTS tab.
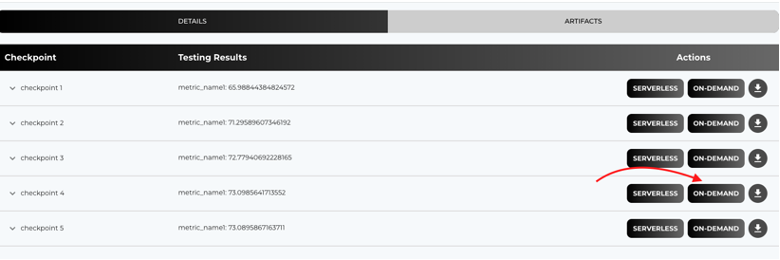
- Select a Checkpoint to Deploy.
Parameter Recalibration
Adjust parameters like do_sample, temperature, max_new_tokens, etc. to finetune the model's response behavior.
- do_sample: Enable sampling for more varied outputs.
- temperature: Increase for more creativity, decrease for more deterministic responses.
- max_new_tokens: Limit the length of generated responses.
- top_p and top_k: Control the diversity of the output.
Best Practices
- Start Small: Begin with a smaller dataset to validate your setup.
- Monitor Training: Keep an eye on training logs and metrics.
- Iterative Testing: Use the test dataset to iteratively improve your model.
- Data Format: Use the recommended data formats for your chosen model to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.