Testing and Evaluation
Testing Scripts and Evaluation Metrics
Evaluating your fine-tuned model is crucial to understand its performance and make necessary adjustments. Our platform provides options for users to add metric functions and generate evaluation scores.
Providing a Test Dataset
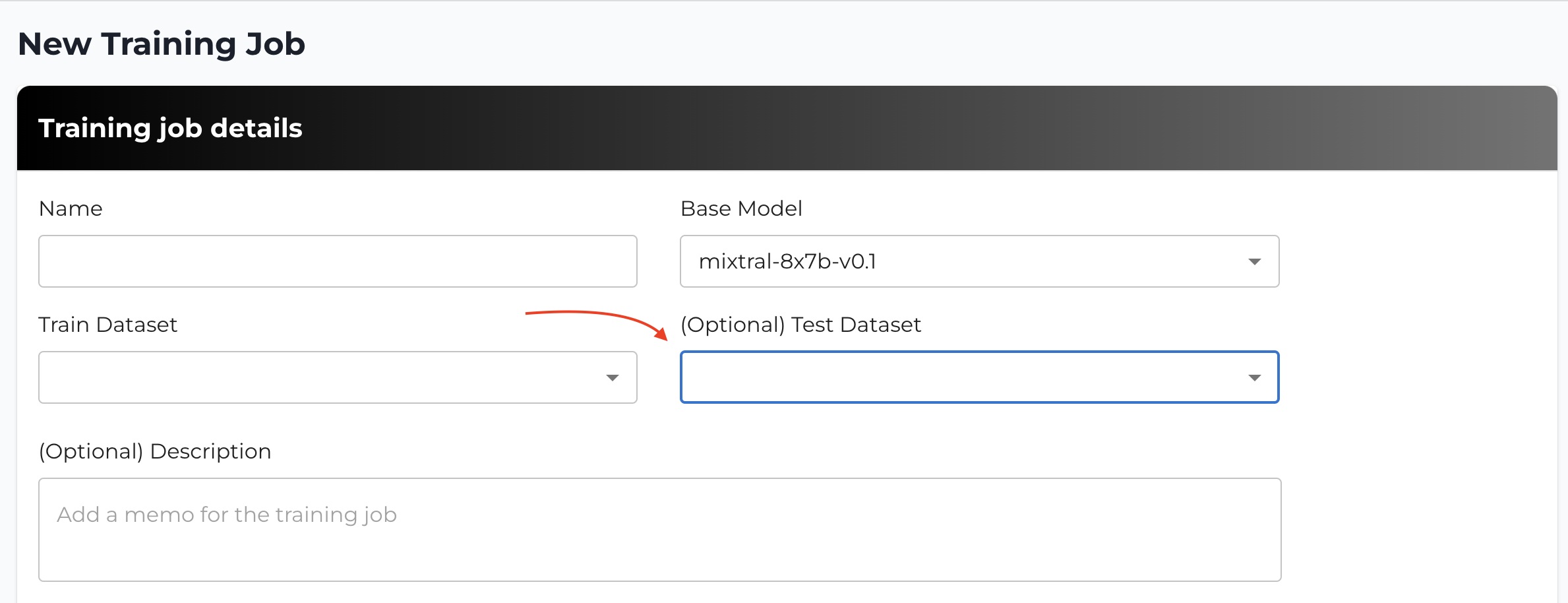
When creating a training job, you have the option to include a test dataset. Including a test dataset allows you to evaluate your model's performance on unseen data during the training process.
How to Include a Test Dataset
- Create a New Training Job: In your model service workspace, go to the training jobs panel and click on + NEW TRAINING JOB.
- Upload Test Dataset: In the training job creation form, you'll find an option to upload a test dataset. Click on Upload Test Dataset and select your test dataset file.
- Dataset Format: Ensure your test dataset is in the same format as your training dataset (CSV or JSONL) and follows the dataset preparation guidelines.
Using Custom Testing Scripts
Our platform allows you to edit the default testing script or upload your own to evaluate your model using specific criteria.
How to Edit the Testing Script
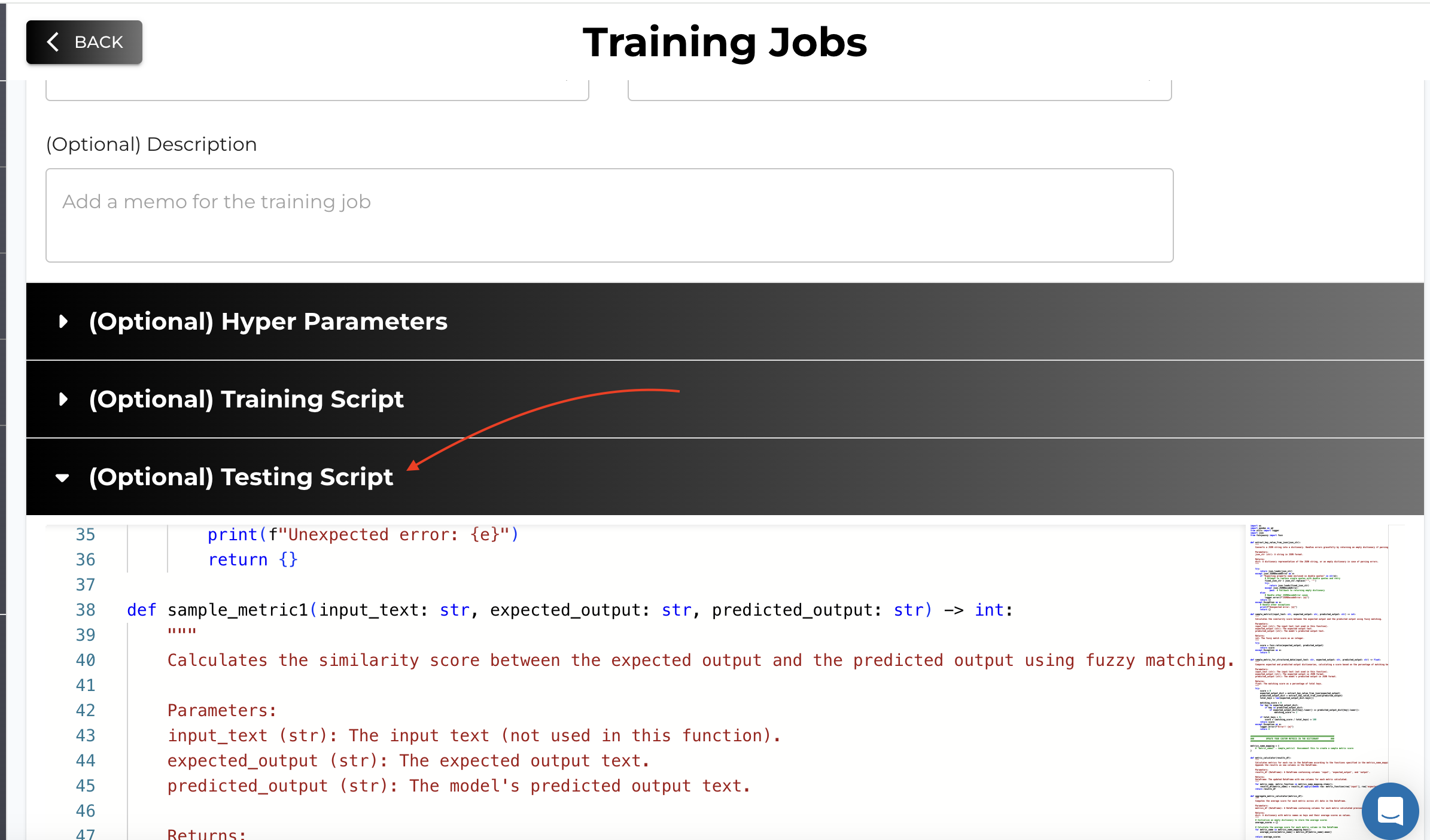
- Advanced Options: In the training job creation form, scroll down to the Advanced Options section.
- Edit Testing Script: Click on the Edit Testing Script button to open the default testing script editor.
- Modify Metric Functions: Update the script by adding your custom metric functions in the specified format.
Note: The default testing script contains placeholder functions where you can insert your custom metrics. Ensure that your functions adhere to the expected input and output formats.
Writing Custom Metric Functions
When creating or editing your testing script, you can define custom metric functions to generate evaluation scores.
Format for Custom Metric Functions
- Function Signature: Each metric function should accept three parameters:
input_text,expected_output, andpredicted_output. - Return Value: The function should return a numerical score (e.g., integer or float) representing the metric.
Example of a Custom Metric Function:
def sample_metric(input_text: str, expected_output: str, predicted_output: str) -> float:
# Your custom metric calculation
score = compute_some_metric(expected_output, predicted_output)
return score
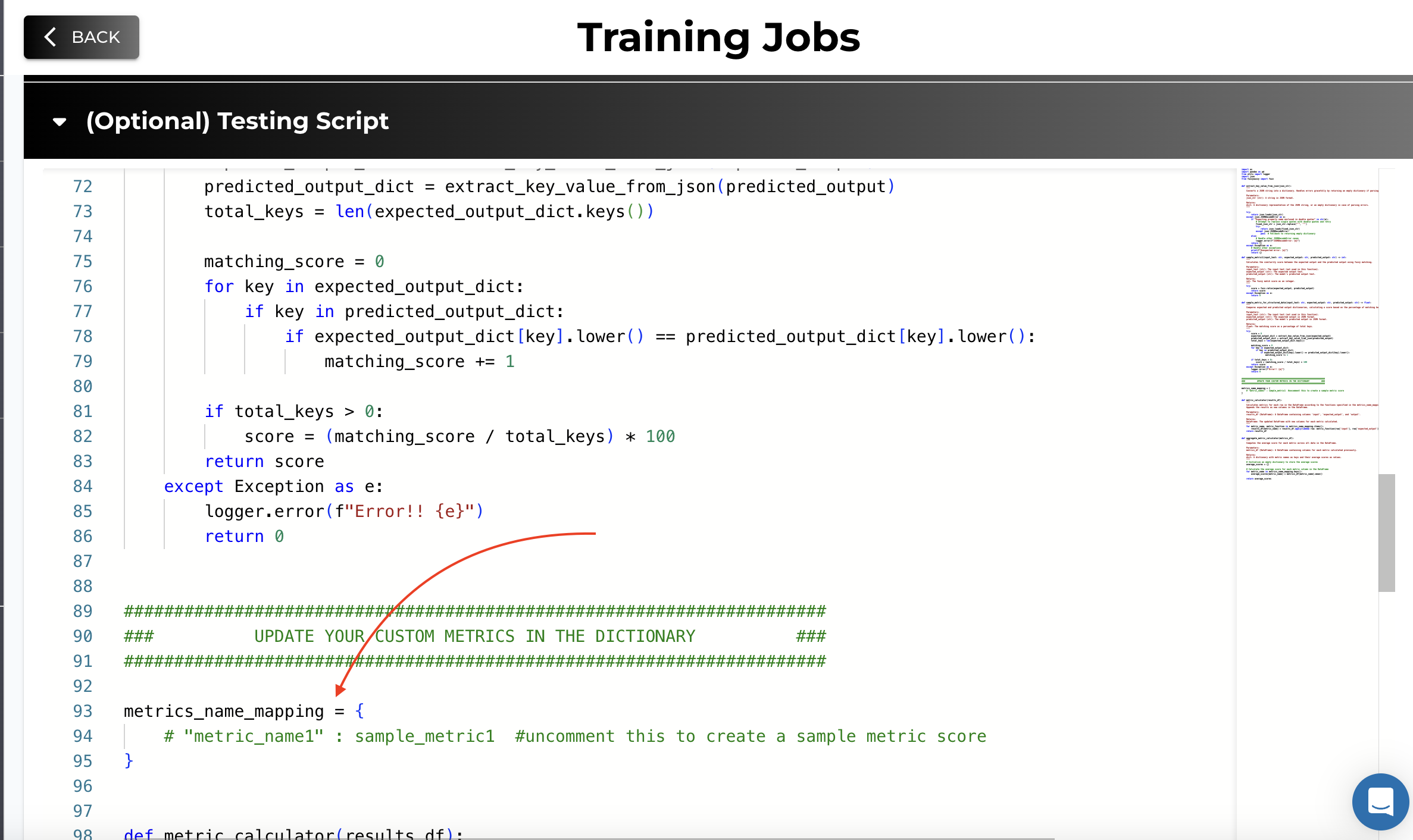
Updating the Metrics Dictionary
In the testing script, there's a dictionary named metrics_name_mapping where you register your custom metric functions.
Example:
metrics_name_mapping = {
"metric_name1": sample_metric,
# Add more metrics as needed
}
Instructions:
- Add Your Metrics: Replace "metric_name1" with the name of your metric and sample_metric with your function name.
- Multiple Metrics: You can add multiple metrics by including additional key-value pairs in the dictionary.
Generating Evaluation Scores
After training, the platform will use your testing script to evaluate the model on the test dataset.
- Per-Checkpoint Evaluation: Evaluation is performed at each checkpoint or epoch during the training process.
- Results Display: The generated results and evaluation scores are displayed on the UI, allowing you to track your model's performance over time.
- Accessing Results: Navigate to the Training Job Details page to view the evaluation results.
Interpreting the Results
- Generated Outputs: For each test input, the platform displays the model's predicted output alongside the expected output.
- Metric Scores: The calculated metric scores are shown, helping you assess the model's performance quantitatively.
- Performance Over Epochs: By evaluating at each checkpoint, you can observe how the model improves (or not) over time.
Best Practices for Testing Scripts
- Consistency: Ensure that your testing script uses the same preprocessing steps as your training data.
- Error Handling: Include error handling to manage unexpected inputs or issues during evaluation.
- Performance Optimization: Write efficient code to reduce evaluation time, especially for large datasets.
- Validation: Test your custom metrics locally before uploading to ensure they work as expected.
Tips for Effective Evaluation
- Align Metrics with Objectives: Choose evaluation metrics that best reflect your model's intended use case.
- Use Representative Test Data: Your test dataset should be representative of the data the model will encounter in production.
- Monitor Overfitting: By evaluating on a separate test dataset, you can detect if the model is overfitting the training data.
Note: This testing script included on the platform is a template to guide you in writing your testing script. Ensure your actual script includes all necessary imports and handles any exceptions appropriately.
By utilizing custom testing scripts and evaluation metrics, you can gain deeper insights into your model's performance and make informed decisions to enhance its capabilities. Remember that when you include a test dataset, the platform displays the generated results along with any metric function scores you have included, and these results are available at each checkpoint or epoch during the training process.